Asterisk ZRTP Developers Guide
1. ZRTP Sessions and streams
The protocol data has a tree-like structure. At the top of the tree is the ZRTP global context. It contains a list of the sessions that have been created, and some crypto-data and synchronization routines. The lower layer contains ZRTP sessions. From the perspective of the user, a ZRTP session is a connection between two ZRTP endpoints, providing storage for ZRTP streams, and an SAS value to verify the key exchange. A ZRTP stream looks like an encrypted tunnel for each kind of media stream within the call.A ZRTP session is established by a single DH stream. The session may be extended by using "Multistream" mode. Since the ZRTP protocol is stream-oriented, it is the stream context which is the main operant for most ZRTP functions.
2. Integration details
2.1 Architecture
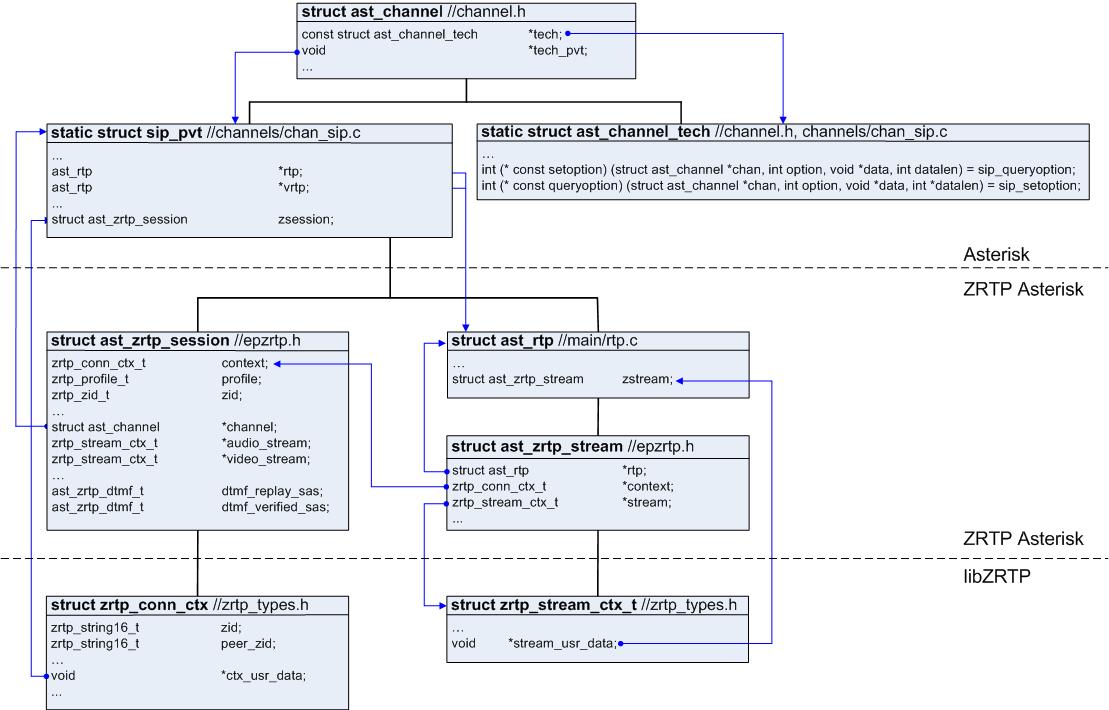
ZRTP Asterisk module architecture
2.2 Entry points
2.2.1 Asterisk is in Man in The Middle mode
In this mode Asterisk stands between two points and acts as a bridge. There are actually two calls: point1-Asterisk and Asterisk-point2.1) Loading res_zrtp.so module
load_module() // res/res_zrtp.c -> ast_zrtp_lib_initialize() // res/res_zrtp.c ...
2) Releasing res_zrtp.so module
-> unload_module() // res/res_zrtp.c st_zrtp_lib_release() // res/res_zrtp.c ...
3) Enabling ZRTP
This procedure is used to separate MiTM and PassThrough modes of Asterisk. ZRTP processing should be present only in MiTM mode.
.. ast_bridge_call() // res/res_features.c ast_channel_bridge() // main/channel.c ast_generic_bridge() // main/channel.c ... //enable ZRTP for both cannels -> g_zrtp_enable->ast_zrtp_enable_zrtp(c0) g_zrtp_enable->ast_zrtp_enable_zrtp(c1) ...
4) Detecting ZRTP-capability of endpoints
We consider an endpoint to be ZRTP-capable if a special SDP tag has been received from this endpoint.
.. sipsock_read() // channels/chan_sip.c handle_request() // channels/chan_sip.c process_sdp() // channels/chan_sip.c ... //set zrtp_capable flag -> p->zsession.zrtp_capable=1 ...
Also we consider an endpoint to be ZRTP-capable if a ZRTP-hello packet has been received from this endpoint.
.. ast_read() // main/channel.c __ast_read() // main/channel.c sip_read() // channels/chan_sip.c sip_rtp_read() // channels/chan_sip.c ... ast_rtp_read() ... //analyze packet type and set zrtp_capable flag -> get_packet_type() p->zsession.zrtp_capable=1 ...
5) Initializing a ZRTP channel
.. sip_new() // channels/chan_sip.c ... //ZRTP channel initialization -> g_zrtp_enable->ast_zrtp_init_zrtp_channel()
6) Deinitializing a ZRTP channel
We deinitialize a ZRTP channel when the sip channel is destroyed to release allocated resources.
.. sip_destroy() // channels/chan_sip.c __sip_destroy() // channels/chan_sip.c ... //Deinitialize ZRTP session -> g_zrtp_enable->ast_zrtp_done_zrtp_channel(); ...
7) Start ZRTP channel
If a ZRTP channel hasn't been started yet we try to start a ZRTP channel with every RTP packet.
.. ast_read() // main/channel.c __ast_read() // main/channel.c sip_read() // channels/chan_sip.c sip_rtp_read() // channels/chan_sip.c ... //try to start ZRTP channel every RTP packet -> g_zrtp_enable->ast_zrtp_start_zrtp_channel(); ...
8) Enter Secure state
When the ZRTP engine enters the Secure state it calls the zrtp_event_callback() function with the ZRTP_EVENT_IS_SECURE event value.
zrtp_event_callback() // res/res_zrtp.c //process ZRTP secure state -> case ZRTP_EVENT_IS_SECURE: ...
9) Process RTP packets
We have to decrypt RTP data before Asterisk will process it.
.. sip_rtp_read() // channels/chan_sip.c ast_rtp_read() // main/rtp.c ... //process RTP data by ZRTP engine -> g_zrtp_enable->ast_zrtp_read() ...
We have to encrypt RTP data before a packet will be sent.
.. sip_write() // channels/chan_sip.c ast_rtp_write() // main/rtp.c ast_rtp_raw_write() // main/rtp.c ... //peocess RTP data by ZRTP engine -> g_zrtp_enable->ast_zrtp_write() ...
10) Process RTCP packets
We have to decrypt RTCP data before Asterisk will process it.
.. sip_rtp_read() // channels/chan_sip.c ast_rtcp_read() // main/rtp.c ... //process RTCP data by ZRTP engine -> g_zrtp_enable->ast_zrtp_read_rtcp() ...
We have to encrypt RTCP data before a packet will be sent.
Process RTCP sender's report.
.. ast_rtcp_write() // main/rtp.c ast_rtcp_write_sr() // main/rtp.c ... //process RTCP data by ZRTP engine -> g_zrtp_enable->ast_zrtp_write_rtcp() ...
Send RTCP recepient's report.
.. ast_rtcp_write() // main/rtp.c ast_rtcp_write_rr() // main/rtp.c ... //process RTCP data by ZRTP engine -> g_zrtp_enable->ast_zrtp_write_rtcp() ...
11) Insert ZRTP signaling hash value into SDP of outgoing SIP packet
..
add_sdp()
...
-> //insert ZRTP signaling hash
...
12) Update ZRTP signaling hash value received from incoming SIP packet
.. sipsock_read() // channels/chan_sip.c handle_request() // channels/chan_sip.c process_sdp() // channels/chan_sip.c ... -> //update ZRTP signaling hash based on incoming packet ...
13) Process DTMF signals
We use DTMF signals to get commands from a ZRTP peer, such as to replay SAS values, mark a peer as verified, etc. All DTMF signals caught by a ZRTP engine will be passed to Asterisk transparently.
.. ast_bridge_call() // res/res_features.c ast_channel_bridge() // main/channel.c ast_generic_bridge() // main/channel.c ast_read() // main/channel.c ... -> //process DTMF signals by ZRTP engine ...
2.2.2 Asterisk is in Pass Through mode
In this mode points are exchanging data directly. Asterisk is processing only SIP packets. Because ZRTP packets differ from RTP packets, Asterisk drops them. To prevent this ZRTP uses pass through mode.a) Process ZRTP packets
.. p2p_rtp_callback() // main/rtp.c bridge_p2p_rtp_write() // main/rtp.c ... -> //process ZRTP packets in Pass Through mode
2.3 Callback details
The ZRTP engine process is accompanied by zrtp_event_callback() calls with appropriate event values. After a ZRTP session starts there are three possible stable states of each ZRTP stream of the session: Secure, Clear, and Error. When each state is entered, it is indicated by the corresponding callback.
- Error state. This state indicates software or hardware errors in the ZRTP protocol. This state isn't processed by the current Asterisk ZRTP implementation.
- Clear state. The stream may enter this state when the 'Switch to playing RTP' option is enabled in Zfone or when the allowclear option is enabled in Asterisk ZRTP. During an Asterisk call, both options are disabled, so the stream can't enter this state. Therefore this state is also not implemented in Asterisk ZRTP.
- Secure state. In ZRTP Asterisk mode, there are different ways of entering the Secure State. In the ENDPOINT mode, one point is SIP supported and ZRTP capable, and the other is not SIP supported and therefore not ZRTP capable. SAS values will be played to the non-ZRTP point by automated speech. In the MITM mode both points are SIP supported. If one of the points isn't ZRTP capable, then the SAS values will be played to this point by automated speech. If both points are ZRTP capable, the SAS values will be transferred to one of points according the rules described in the ZRTP draft. In ENROLLMENT mode the ZRTP Asterisk engine checks whether the point is already enrolled and sends appropriate control frames which are processed in the Enrollment application.
2.4 Implementation details
The ZRTP Asterisk module encrypts RTP/RTCP payload only. RTP/RTCP headers stay unchanged. The ZRTP Asterisk module doesn't encrypt SIP and H323 traffic.Cache implementation
The current implementation of ZRTP for Asterisk uses the default cache implementation from libzrtp. The cache is stored in memory and is flushed to a binary file periodically and when the zrtp library is released. The advantage of using the default cache implementation is simplicity. On the other hand, the default cache implementation isn't intended to service multiple zrtp peers. It is recommended that an alternative cache implementation is used for better perfomance and larger load capacity, e.g. B-trees or databases.
Timeout handling
The ZRTP module has its own timer implementation. This timer is used by the ZRTP library for resending packets in the zrtp stream after a specified time. There is no separate thread for timeout handling. To handle timeouts, the ast_zrtp_process_timeout() function is called. This function is called for every incoming or outgoing packet.
ZRTP Protocol packet sending
To send a ZRTP protocol packet, the zrtp library calls the zrtp_send_rtp() function. ZRTP for Asterisk has the zrtp_send_rtp() implementation. It calls ast_zrtp_sendto() which sends the data over the connection in a UDP sendto system call.
System-dependent functions
The ZRTP library has the default implementation of system-dependent functions (such as memcpy, memset, etc). The default implementation of system-dependent functions is also used in the ZRTP Asterisk module.
2.5 Enrollment application
The enrollment process is handled by the Enroll_zrtp application implemented in the app_enroll_zrtp.so module. The Enroll_zrtp application should be executed in a special well-known extension. This application sets up a ZRTP session between a ZRTP peer and Asterisk in ENROLLMENT mode:
..
ast_channel_setoption(chan, AST_OPTION_ENROLL_ZRTP, NULL, 0, 0); // apps/app_enroll_zrtp.c
..
Then it enters a loop to wait for control frames.
When a ZRTP stream enters the Secure state (zrtp_event_callback() with ZRTP_EVENT_IS_SECURE event value) it checks whether the ZRTP peer has already been enrolled. If the ZRTP peer has already been enrolled, an AST_CONTROL_ZRTP_ALREADY_ENROLLED control frame will be sent.
If the ZRTP peer hasn't yet been enrolled, an AST_CONTROL_ZRTP_ENROLLMENT_SECURE control frame will be sent.
If a non-ZRTP point tries to call a enrollment extension, it will be detected and a zrtp_event_callback() with the event value ZRTP_EVENT_NO_ZRTP_QUICK will be called. On this event the ZRTP Asterisk module sends an AST_CONTROL_ZRTP_NO_ZRTP_QUICK control frame.
Behaviour of the Enroll_zrtp application on arrival of different control frames:
- AST_CONTROL_ZRTP_ALREADY_ENROLLED: play appropriate automated voice notice and then hang up.
- AST_CONTROL_ZRTP_ENROLLMENT_SECURE: play appropriate automated voice notice and then wait for the caller to hang up.
- AST_CONTROL_ZRTP_NO_ZRTP_QUICK: play appropriate automated voice notice and then hang up.